Data Analysis Promises Much
In 2022 alone at least 94 zettabytes of data will be generated. One zettabyte is 270 bytes – that’s 2 to the power of 70 or 1.18 multiplied by one sextillion (21 zeroes!).
The figure stood at 64 zettabytes in 2020, 79 in 2021, and is expected to rise to 175 zettabytes by 2025.
This is on top of the massive amounts of existing data, 90% of which was generated in the last 2 years only.
Given these jaw-dropping statistics, it is easy to see why Data Science and Analytics are some of the most promising career options in the coming decades.
There will be a surge in demand for data-based jobs in almost every industry, as businesses grapple with how best to harness the incredible amounts of data they hold.
We will discuss the various opportunities and roles available in this field, and what it takes to execute them efficiently.
Careers in data science involve finding, editing, storing, analysing, managing and improving data. We have previously discussed the difference between data scientists and data analysts. All roles within the data sphere have evolved from purely academic pursuits to essential cogs in the business machine.
Soft Skills
The basic soft skills required for working in the data science field are:
- A curious mind
- Innovation, vision, and empathy to understand what the client needs
- Passion to keep learning new skills and improve your existing ones
- Mathematical thinking etc.
- Problem-solving orientated mind
- Creativity and storytelling skills to help you convey your findings clearly and in an interesting manner
You will also need immaculate communication skills to convey your findings in a clear and easily digestible manner so that decision-makers can easily understand and make informed decisions.
As there will always be changes and turnarounds, you must be adaptable and have some business acumen to ascertain what is necessary to sustain and grow in new conditions.
It also requires some interdisciplinary skills, and you must be proficient in at very least two of the following skills:
- Statistics
- Programming
- Data storage and retrieval
- Analytics
- Visualisation
- Domain-specific knowledge
Technical Skills
To store and process such huge volumes of data, and to extract meaningful insights, you need to be across some very new and sophisticated tools.
Some tools and technologies frequently used in data science and analytics are:
- Relational databases like MySQL, Oracle, SQLServer etc.
- Used to store the inherently relational data
- NoSQL Databases like MongoDB, Neo4J and Cassandra
- Used to store the non-relational or unstructured data
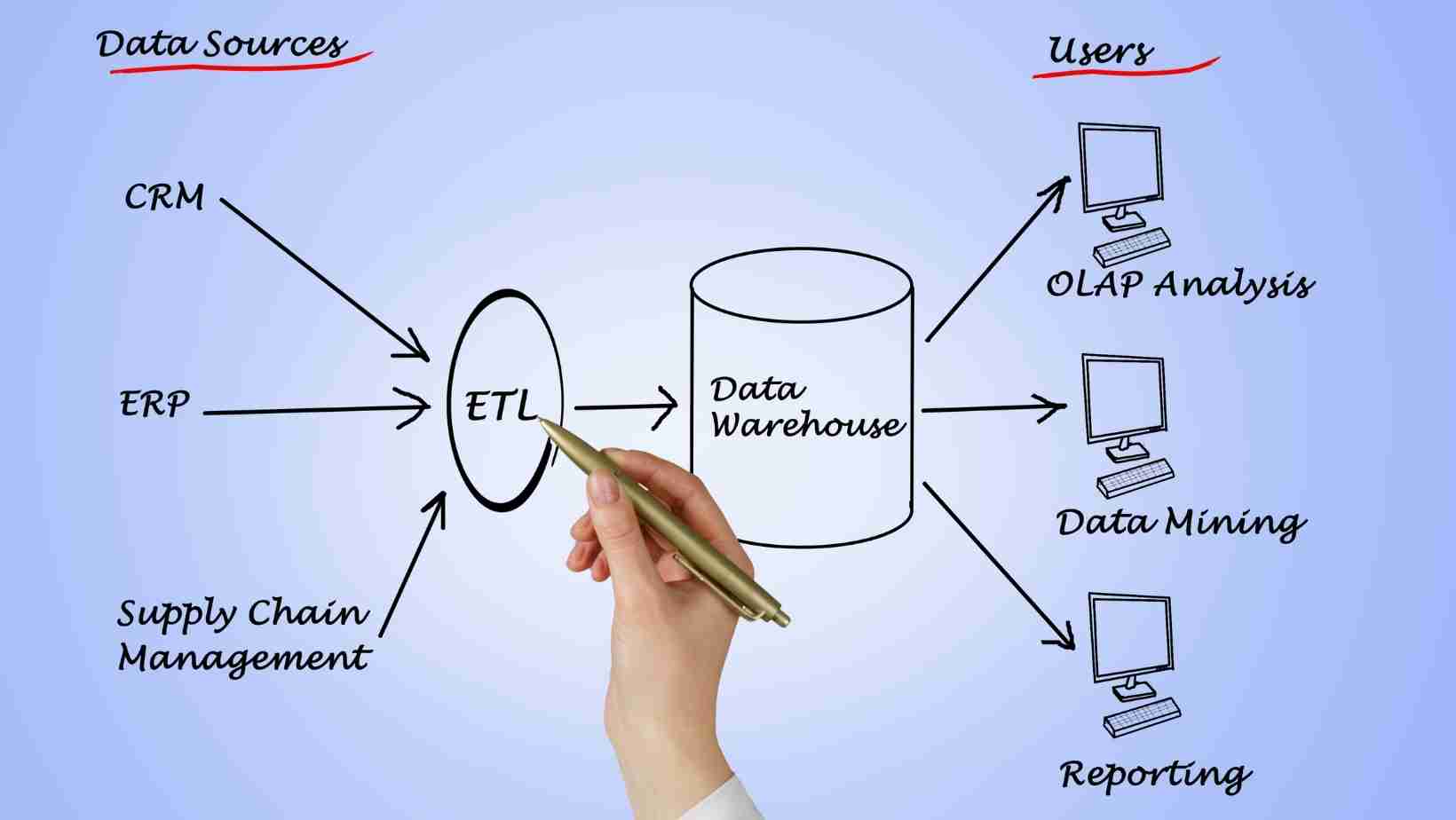
- Data Warehousing tools like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Microsoft Azure and Snowflakes etc.
- A data warehouse is a multi-dimensional data store that houses data in many formats, where the data is sourced from heterogeneous sources.
- A Data warehouse attempts to create a unified system of truth for the organisation and involves sourcing/staging/storing/versioning/retrieval of data.
- Programming languages like Python, R and Java
- Used to run programs that will process data and compute statistics, according to your unique business needs.
- Advanced-Data Analysis & Visualisation tools like Power BI, Tableau, QlikView and Excel etc.
- Used to run analytics, uncover trends/anomalies, and create intuitive visualisations.
- AI and Machine learning
- Used to create artificially intelligent algorithms/software that learn from the data they receive and teach themselves to improve as the incoming data/requirements change.
Together, these soft and technical skills will help you assist the stakeholders to make data-driven decisions that solve key business problems and fuel/sustain growth.
Potential Roles
Data Scientist
Data scientists tend to have many duties, including creating data and machine learning models, creating a framework for analysis, running data testing and experiments, and continuing to improve and optimise their frameworks. This is all in pursuit of generating accurate and actionable business insights.
Once you know what and how data is to be collected and processed, the next role that naturally comes into play is that of a Data Architect.
Data Architect
A Data Architect designs the data structures and data pipelines an organization needs.
Their responsibilities are to effectively acquire, organise, analyse, manage, and utilise data.
They then design data warehouses, which includes translating business objectives into a data management framework, defining how data will flow through the framework, and working with other teams and engineers to develop the framework and implement it across the organization.
Data Modeller
A data modeller creates data models, presents data in various ways to make it easier for others to understand, changes previous data models so more people can work with them and tests their models to ensure that they are functional.
Data Manager
A Data manager is responsible for managing the Data analysis department/practice and acts as a bridge between management and data engineering teams.
The Data Manager could also be responsible for overseeing the creation of a data warehouse, and its management.
Database administrator
Database administrators use specialised software to secure, organise, and store data. The database administrator or DBA oversees the function of all aspects of the database environment to ensure they work optimally. They also work with other data professionals to make sure the database is available for them to complete their jobs.
Also, they make sure that the databases remain in pristine condition to respond to queries quickly and to improve the processes such that they consume minimal database bandwidth. Next comes the Data engineers who extract relevant data from the warehouse and process it.
Data Engineer
Not only do Data engineers work with data in its purest form, but they also prune/aggregate/pre-process it for analysts to work on.
They may use various coding languages, including Python, C++ and Java, to read and process different data types.
Data Analyst
Data analysts get specific subsets of data relevant to the problem to be solved or the analysis to be performed.
Data analysts are proficient in mathematics/statistics, and they use their knowledge to answer specific questions like "What will be the seasonal downswing in demand for the next year?"
Once you have the statistics/numbers from the Data analyst, there is a need to correlate them with the business processes.
Business intelligence analysts
Business intelligence analysts are focused on using data to improve an organisation and organisational processes, they are also expected to translate their data analysis into actionable strategies to improve the business—and present their strategic analysis to leadership. A Business analyst also plays a key role in formulating the requirements/questions for the data analyst to work on.
A Business intelligence analyst is a crucial role, as they are the best ones to formulate strategies according to the available resources, seasonal swings, government policies and customer sentiment.
Another highly skilled role is that of a Machine Learning Engineer.
Machine Learning Engineer
A Machine Learning Engineer creates machine learning models, backed up with artificial intelligence software.
Machine Learning Engineers are highly skilled programmers who code programs that can work independently, learn on their own and give automated predictions.
They are also responsible for updating and improving these programs in coordination with the Data scientist and Business intelligence analyst.
If you think you already possess some of the above skills or are ready to develop a subset of them, then data science and analytics could be a fruitful career for you.
As previously discussed, a grounding in programming languages such as Python or R can be a valuable tool. Join one of our many courses today. Power BI courses can also help further your career, regardless of your field.